| Precision Casting Production Process and Control
Purpose:
Specify the process inspection points and the scope of each inspection point that can be implemented and tested in the production process, so that the products can complete the specified inspections and experiments before the process is transferred and leaving the factory, to ensure that the quality of the products meets customer requirements.
Precision casting production is divided into four major processes: wax injection, shell making, furnace front, and casting.
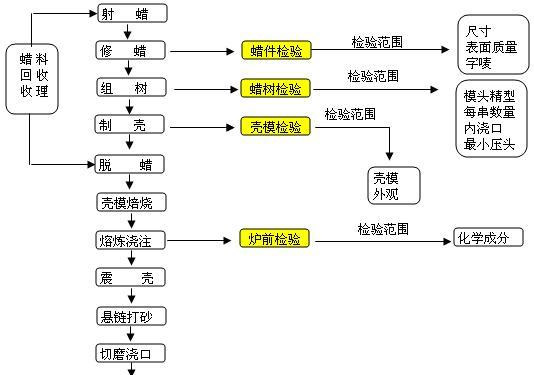 
Wax injection:
The wax used in our company is a precision casting special K-512 made by Japan Paraffin Wax Co., Ltd. The production of wax parts adjusts the injection process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and holding time according to different sizes and structures; The commonly used process parameters for wax injection are: wax injection pressure: 15-25Kg/c ©O, cooling water temperature: 20-24 ¡æ. The ambient temperature of the wax injection workshop is: 23 ¡À 2 ¡æ. For wax parts with large size, to reduce surface depression caused by body shrinkage, cold wax blocks are usually used for filling.
Wax repair:
The injected wax pieces can be repaired after about 3 hours of storage. The wax pieces should be repaired to remove flying, sharp corners, edges, and injection ports. For small areas of defects, repair wax should be applied. If deformation, insufficient filling, excessive bubbles, etc. are found, they should be scrapped. Blow out the wax fragments on the surface of the wax pieces, and pay attention to the clear font and mark on the wax pieces
The ambient temperature for wax injection is 23 ¡À 2 ¡æ

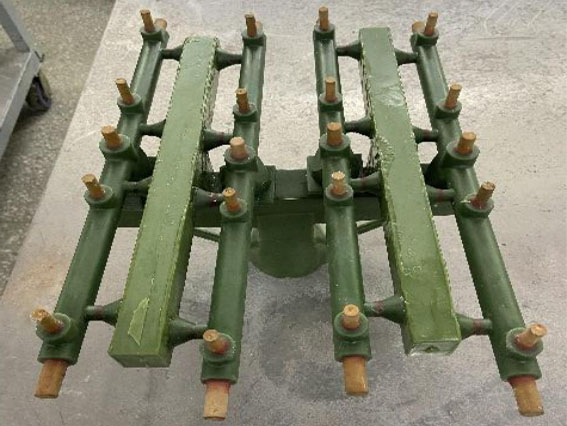
Group Tree:
According to the requirements of the assembly tree process diagram, melting the wax parts into the sprue (mold head) is called assembly tree.
The design of the tree assembly process should select appropriate tree assembly schemes based on wax pieces of different sizes and structures; The inspection content and standards are based on the group tree process diagram, mainly including:
1. Type of die head;
2. Number of each string;
3. Model and quantity of internal gate;
4. Minimum pressure head
Precautions for tree assembly: No welding gaps are allowed on each wax tree
 
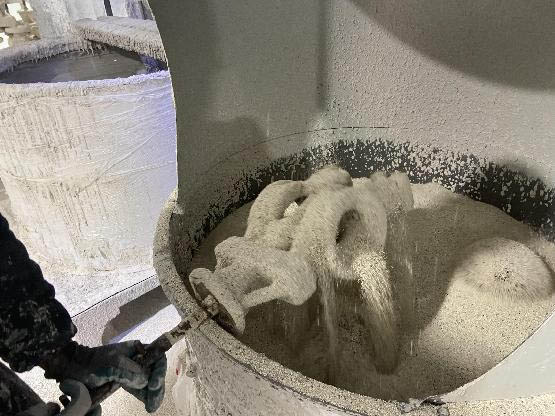
clean:
The wax tree that has been assembled must be cleaned of oil stains, release agents, and other debris on the surface of the wax; The cleaning solution uses a cleaning agent, and the cleaning process is as follows: immerse the wax tree in the cleaning agent, move it up and down two to four times, lift it up and immerse it in clean water for rinsing, self check the cleaning effect, and after achieving the effect, cool the trailer dry. The cleanliness of the wax surface directly affects the coating performance of the shell mold surface slurry (and the surface quality of the casting)
Generally, cleaned wax trees should:
a. The surface has no wax or grease luster;
b. There is no phenomenon of roughness or melting state caused by excessive erosion on the surface;
Shell making:
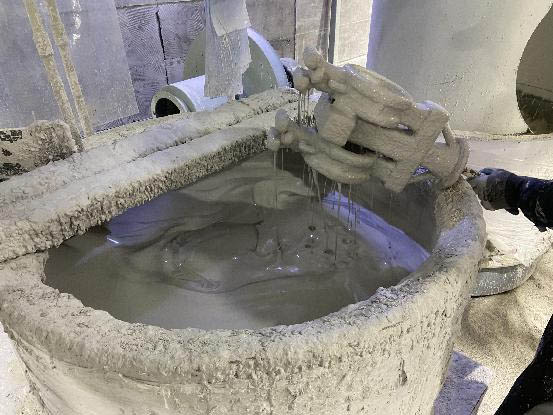
Materials: zirconium powder, zirconium sand, mullite, silica sol, and some auxiliary materials
1. The shell making process involves soaking in paint, spraying (applying) sand, and drying; Repeat multiple times to obtain a multi-layer shell with a certain thickness
2. Factors affecting shell drying: environmental temperature, humidity, ventilation conditions, shell material, product shape and thickness, etc
3. The ambient temperature is generally controlled at 22-26 ¡æ; High environmental temperature can accelerate the evaporation of water and shorten the drying time of the shell mold; However, excessively high temperatures can affect the thermal expansion and stability of wax parts, thereby affecting the dimensional accuracy of castings and resulting in deformation
4. Environmental temperature has a significant impact on dryness. The higher the humidity, the longer the drying time. It is most ideal to control the relative humidity in the shell making workshop between 40% and 60%; The relative humidity of the surface layer can be controlled between 50% and 70%
5. The influence of wind speed on drying speed is also significant. If the wind speed is high, the drying time will be short, but the wind speed should not be too high, as it will blow off the sand particles on the module
6. When making shells, attention should be paid to using shell molds with uniform thickness, solid adhesion, sufficient drying, and certain strength
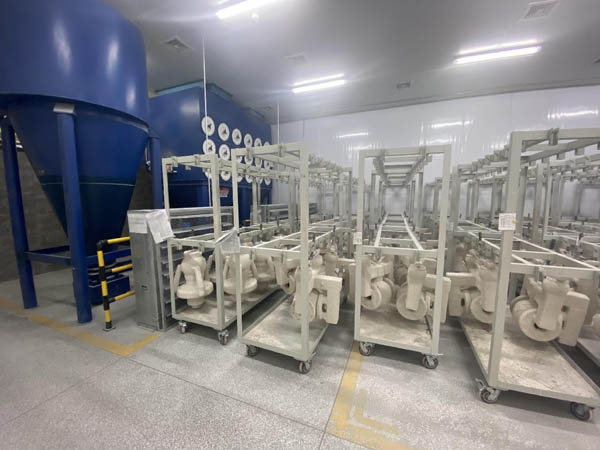
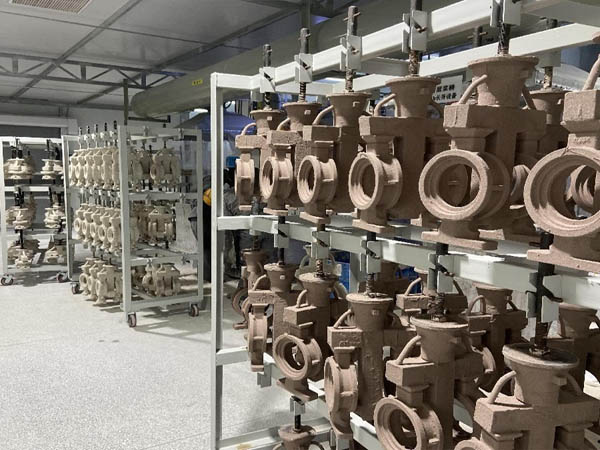
   
Dewaxing:
Our company uses high-pressure steam dewaxing method. The temperature in the dewaxing steam kettle is about 150-175 ¡æ, the steam pressure in the kettle is 7-8kg/c ©O, and the dewaxing time is 8-15 minutes; The setting of each parameter depends on the specific situation such as the size of the shell mold structure.
The process of wax recovery:
The wax liquid is filtered through a filter screen from the mixing drum and then fed into a static drum. The static temperature is 70-100 ¡æ, and the static time is greater than 8 hours before starting to discharge. The discharged wax liquid is then subjected to vacuum wax recovery equipment for dehydration and impurity removal, and the recovered wax is transported to the wax ejector for use.
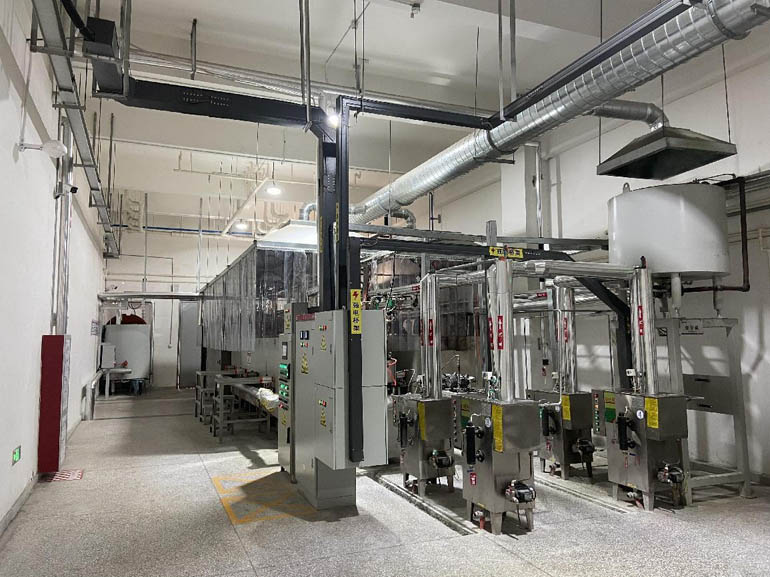
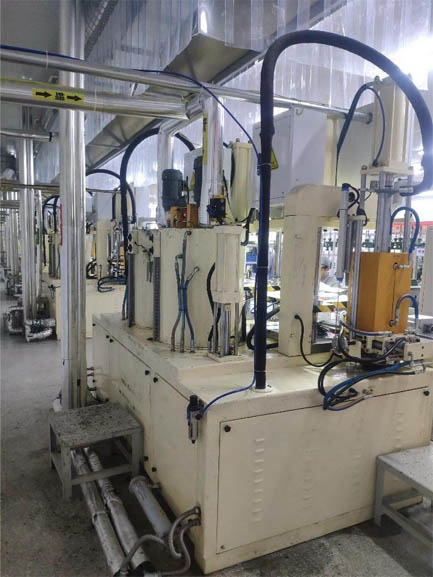
 
Baking of shell molds:
Due to the need for high-temperature pouring in precision casting shell molds, the pouring temperature is generally above 1530 ¡æ. Therefore, the shell mold needs to have good high-temperature strength, and therefore the shell mold needs to be baked to improve high-temperature strength; The roasting temperature is usually 950~1050 ¡æ. In order to fully burn the shell mold, it is necessary to keep it warm for at least 30 minutes after reaching the temperature
Several favorable aspects for the quality of castings after shell mold roasting:
a. Burn off the combustible materials mixed in the shell mold to improve air permeability
b. Burn off the remaining wax, moisture, and gas that have not been completely removed to prevent gas from oxidizing the surface of the casting during pouring
c. High temperature shell mold combined with molten steel can prolong the solidification time of castings in the shell mold
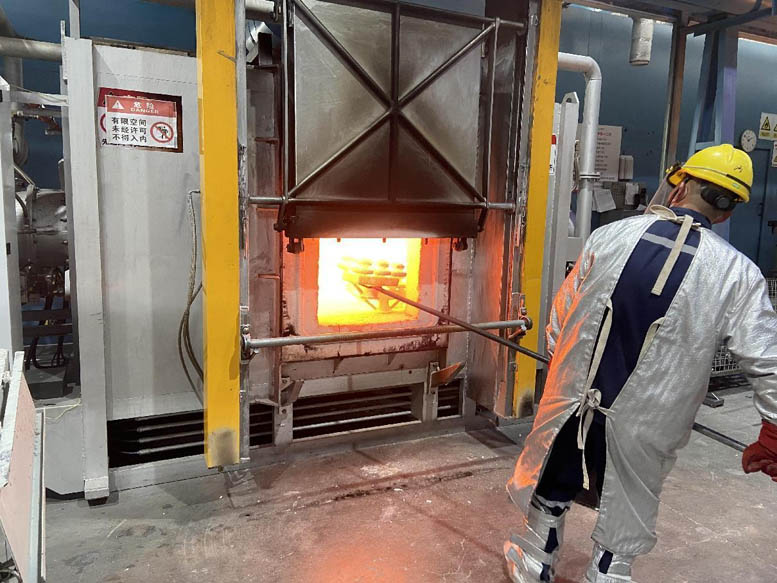

Pouring:
The molten steel poured in shall be proportioned according to the material requirements of the casting (the materials to be mixed include: this material, recycled materials, alloy auxiliary materials and slagging agent). The matched molten steel shall be subject to strict smelting process. Before pouring, the sample shall be drawn and the composition shall be analyzed on the spectrometer. If it does not conform to the material composition, the corresponding alloy auxiliary materials shall be added and adjusted to be qualified
Pouring factors that affect the quality of castings:
a. Pouring temperature;
b. Pouring speed;
c. Shell mold temperature
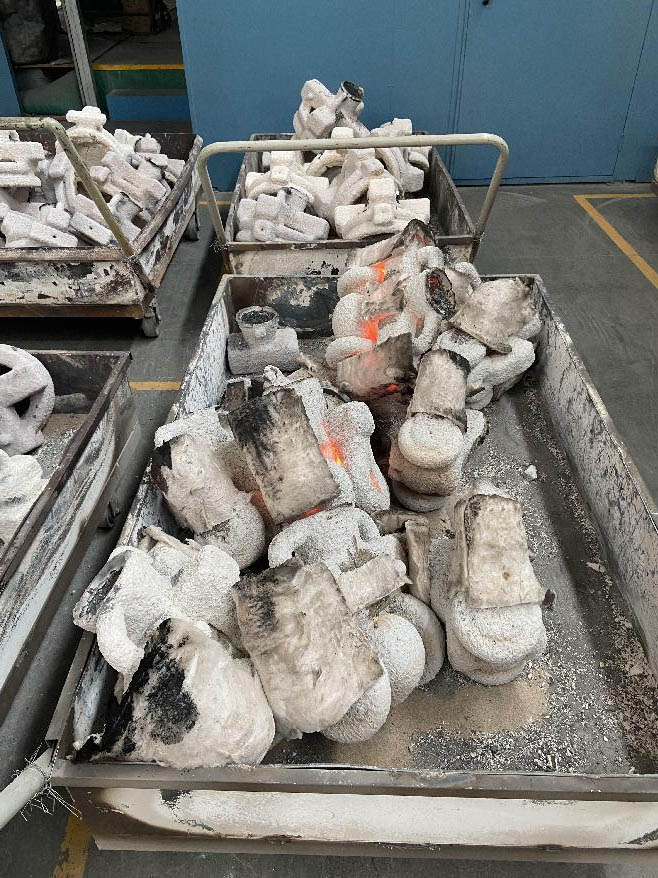
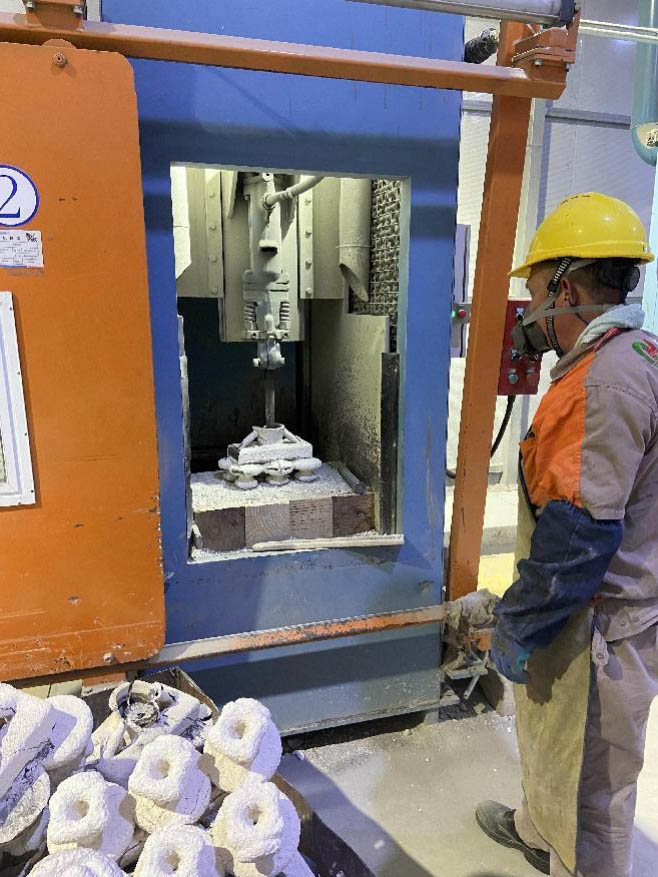
Vibration shell:
After pouring and cooling, the shell can be removed. It is achieved by using a vibrating hammer on a gravity vibrating shell machine to strike the cap opening, causing the shell mold to quickly peel off the steel tree. The vibrating hammer is driven by compressed air
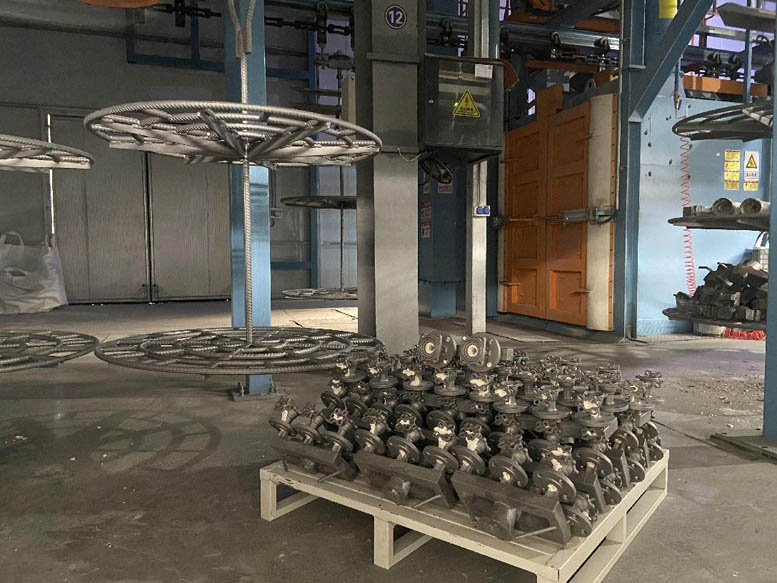
  
Cutting:
1. The cutting method adopts grinding wheel cutting and arc cutting;
a. The cutting area of the grinding wheel blade is flat, and the residual amount of the gate is small;
b. Arc cutting consumes welding electrodes, has a high cost, and the incision is uneven. It is only used when the grinding wheel cannot cut. Wherever possible, gate residues should be minimized to save abrasive and gate grinding time.
2. The cut mold heads should be stacked according to different materials and clearly marked before being fed into the steel silo for future use as furnace materials.
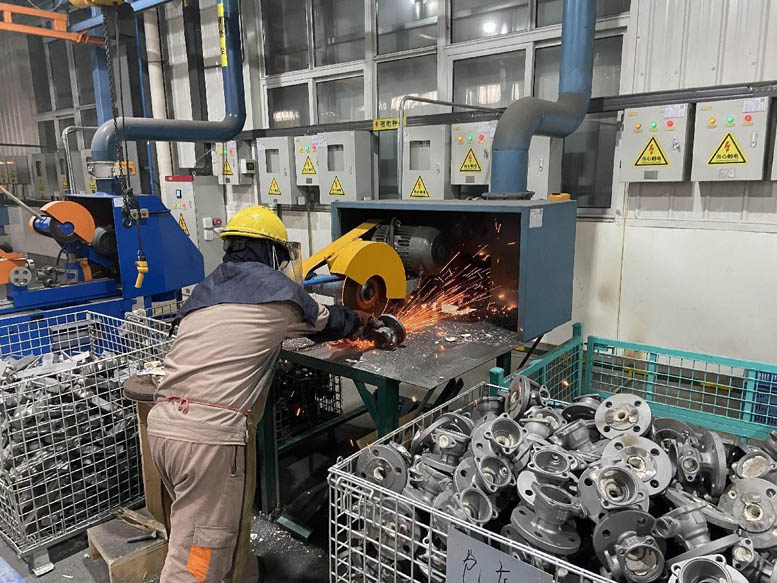

Grinding gate:
The remaining gate after cutting the casting needs to be ground flat, and the burrs and fleshy parts on the casting need to be removed; To avoid affecting the appearance and use of castings, the residual standard of the gate: Generally, the gate can remain ¡Ü 0.5mm on the processing surface; The gate must be ground flush with the original surface of the casting on the non machined surface
Our company uses sandcloth tape to grind the gate. During rough grinding, we use 40 # coarse sand tape (machining surface), and during fine grinding of non machining surface, we use 180 # fine sand tape with a residual thickness of about 0.2mm during rough grinding

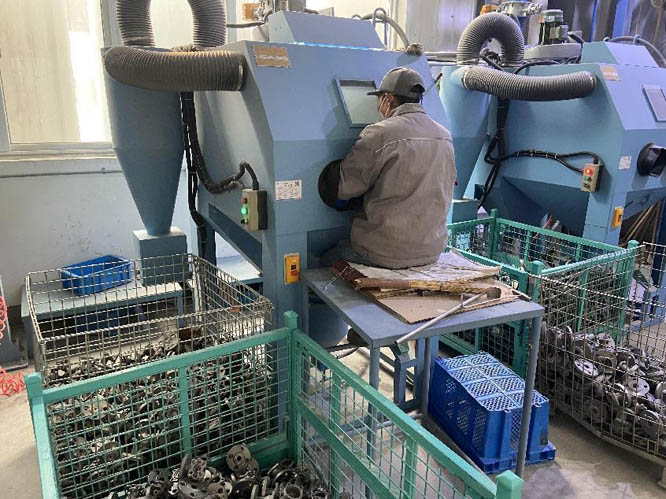
Sand cleaning:
1. Strong sandblasting: Use 80 # alloy steel sand (tungsten carbide: WC) to remove residual shell mold, oxide skin, and sand core from the surface and inner cavity of the casting
2. Suspended chain sanding: Use S170 # steel balls with a particle size of 0.4-1mm to strike the surface of the casting to remove oxide skin and shell mold. The time of the steel ball striking needs to be strictly controlled to avoid affecting the surface quality of the casting.
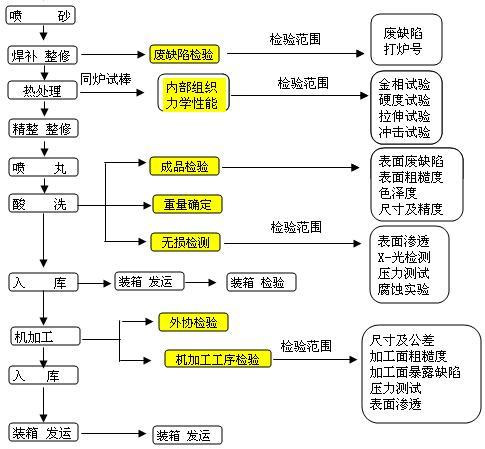
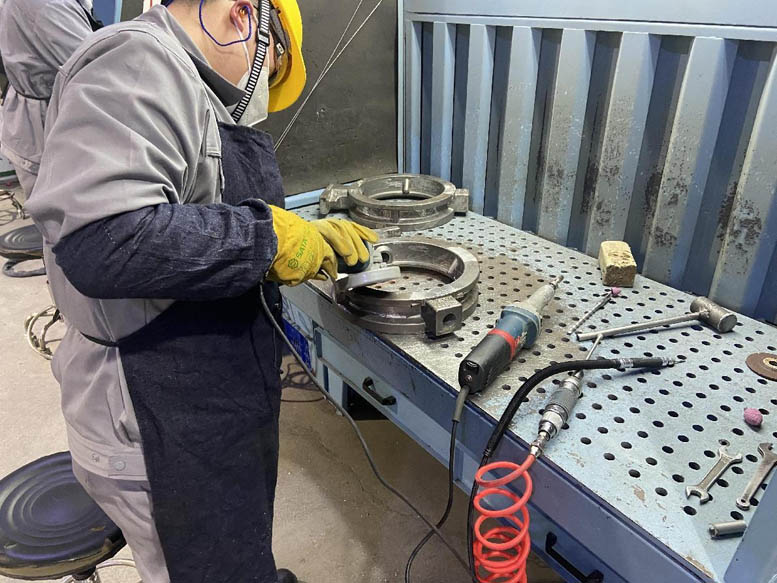
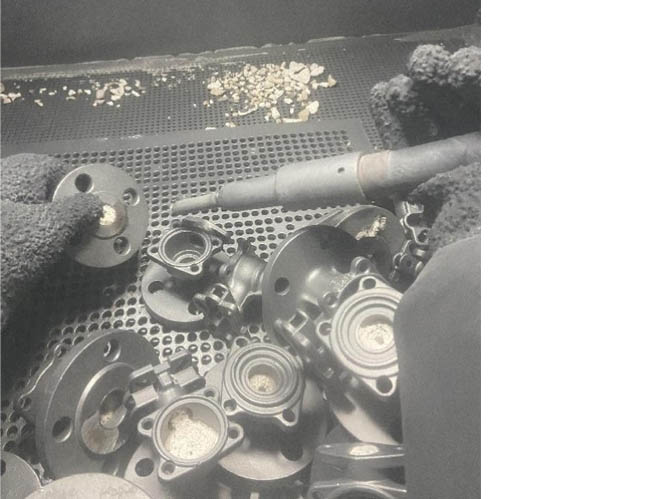  Welding repair and repair:
1. Welding repair of castings: For small defects such as air holes, sand holes, and slag that can be repaired by welding, welding repair repair treatment should be carried out. The material of the welding rod should be the same or similar to the casting. Before welding repair, the oxide skin or debris in the defect area should be completely removed to expose the metallic luster. After welding repair, it is necessary to polish it flat and keep it flush with the original surface
2. Formwork correction: Due to factors such as deformation of wax parts and shell molds, external forces during sanding, and cutting of the pouring system, the geometric shape and size of the castings are not qualified, which requires the use of formwork correction methods for correction; It relies on external forces to cause a certain degree of reverse deformation of the deformed casting, thereby restoring the casting to its qualified geometric shape and size
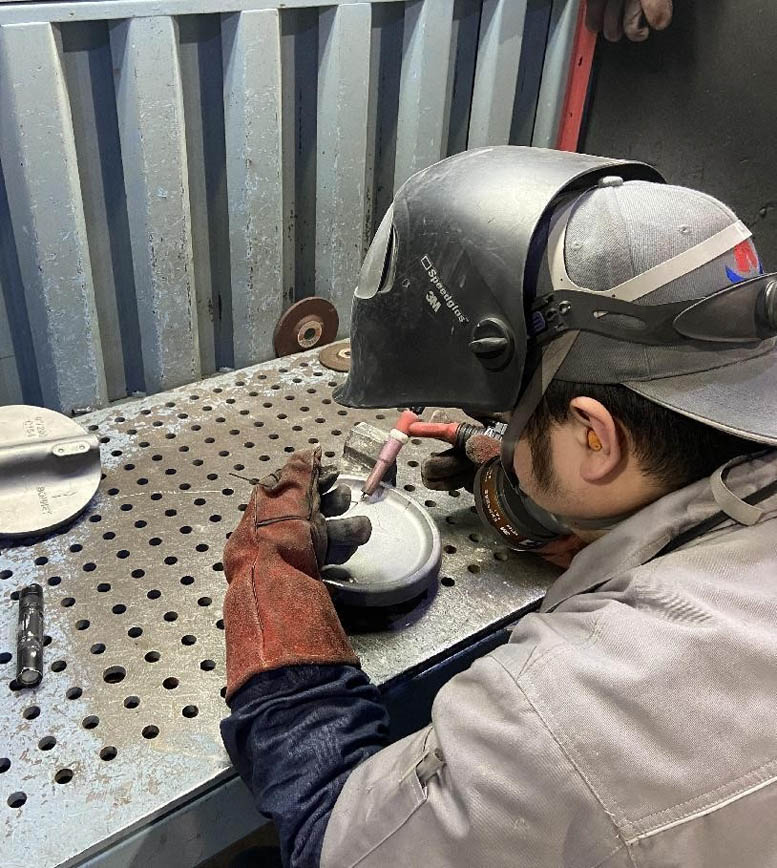
 
Heat treatment:
The grain size of as cast alloys is generally relatively coarse, and there is significant internal stress, especially for castings with complex structures or undergoing shaping correction, the stress is even greater; Therefore, castings need to undergo heat treatment to homogenize and refine their steel structure, eliminate internal stress, and improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance
1. Heat treatment of austenitic stainless steel
The commonly used heat treatment method for austenitic stainless steel (1.4408, CF8M) is solid solution treatment; Its purpose is to obtain single-phase structure, homogenize the structure of steel, dissolve carbonized substances into austenite, and improve its mechanical properties and corrosion resistance;
2. Heat treatment of carbon steel parts
The heat treatment method for carbon steel parts (1.0619, WCB) adopts normalizing treatment. The purpose is to refine the structure, increase strength and toughness, reduce internal stress, and improve cutting performance

Sanding:
After heat treatment, there is a layer of oxide skin on the surface of the casting, which needs to be removed by sandblasting (strong sandblasting and chain sanding)
Pickling:
To present the dazzling appearance of stainless steel, stainless steel castings are cleaned with acid to remove surface oxide scale and form a passivation protective film. After rinsing with water, they are cooled and dried
Inspection and warehousing:
Castings that have completed the joint production process should undergo pre warehousing inspection, and qualified products should undergo warehousing procedures; The warehouse shall classify and place them according to regulations, indicating the quantity, name, specification, material, etc. After receiving the shipment arrangement, they shall be packaged and shipped according to the customer¡¯s packaging requirements |
